The Windows Registry plays a critical role in how your operating system functions. Over time, however, the Registry can become cluttered with outdated or unnecessary entries, leading to performance slowdowns or even system errors. Cleaning the Windows Registry can help optimize system performance, but it’s essential to proceed with caution to avoid unintended issues. This article covers the basics of the Windows Registry, how to use the Registry Editor, and the methods you can use to safely clean it.
What is a Windows Registry?
The Windows registry has been playing a crucial part in most versions of Windows since Windows 95, and it’s also used to help configure programs in Windows XP, Vista, Windows 7, and all the way up to Windows 10 and Windows 11. The Windows Registry is a hierarchical database that stores essential configuration settings and options for the operating system, applications, user preferences, and connected devices. Whenever you make changes to your system – whether it’s installing software, connecting hardware, or modifying system settings – Windows updates the corresponding Registry keys and values.
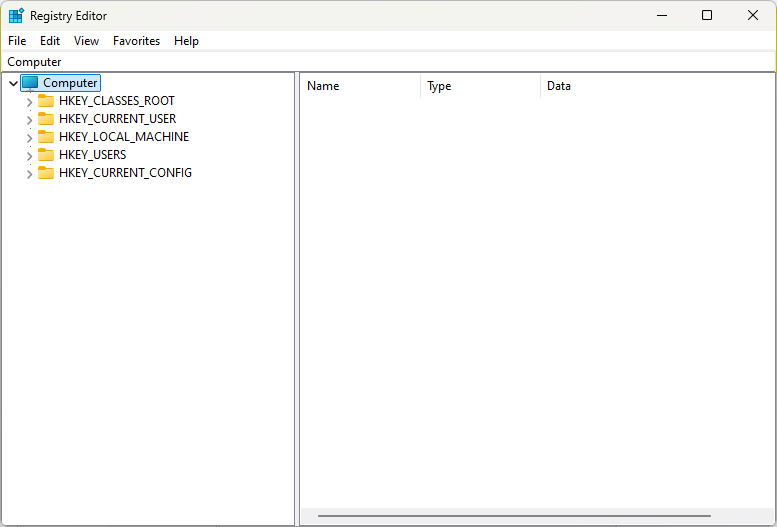
Each Registry entry consists of keys, subkeys, and values that define how software and hardware interact with the operating system. Over time, as programs are installed, uninstalled, or updated, the Registry can accumulate obsolete or corrupt entries. These unnecessary entries can cause slowdowns, errors, or even system crashes if left unchecked.
How to Use the Registry Editor
The Registry Editor is a built-in tool in Windows that allows you to view, modify, and delete registry keys and values. While editing the registry can be risky, it’s often necessary for advanced troubleshooting or customization.
Here’s how to safely open and use the Registry Editor:
- Open the Registry Editor:
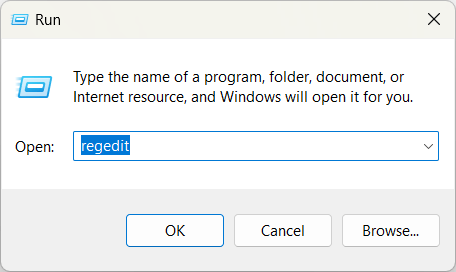
- Press Win + R to open the Run command.
- Type regedit and press Enter.

- If prompted by User Account Control, click Yes to allow access.
- Navigating the Registry. The Registry Editor displays a hierarchical tree structure. The major root keys include:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE (HKLM): Contains settings specific to the local computer.
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER (HKCU): Stores settings related to the currently logged-in user.
- HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT (HKCR): Contains file association information.
- HKEY_USERS (HKU): Stores user profiles.
- HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG (HKCC): Contains information about the current hardware profile.
- Registry Backup: Before making any changes, it’s essential to back up the Registry to avoid irreversible damage if something goes wrong. To back up:
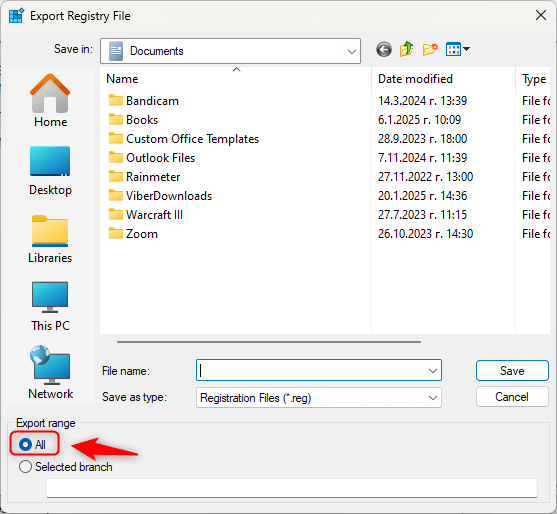
- In the Registry Editor, go to File → Export.
- Select All under Export range to back up the entire registry, or choose specific branches.

- Save the backup file in a safe location.
- Making Changes to the registry:
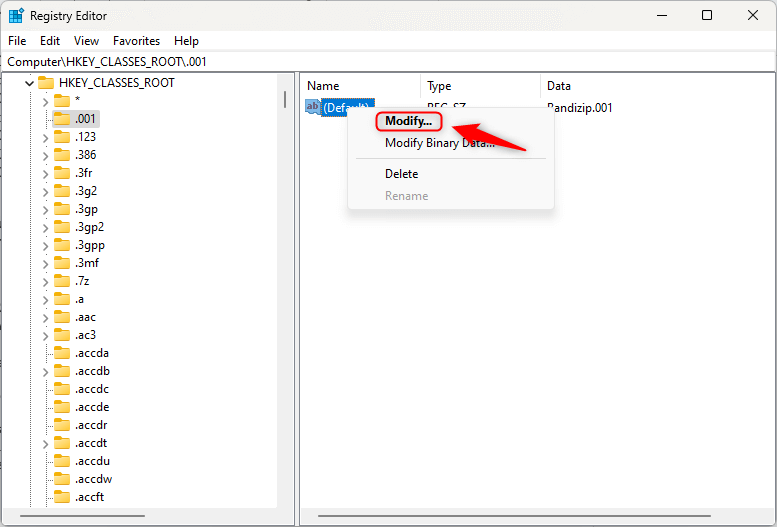
- To edit a key, right-click it and choose Modify.

- You can also delete obsolete keys, but only if you’re certain they’re unnecessary.
- To edit a key, right-click it and choose Modify.
Methods to Clean your Windows Registry
There are several ways to clean your registry, each with varying levels of complexity and safety. Below are the primary methods for maintaining a clean and efficient Registry.
1. Using Disk Cleanup
The Disk Cleanup tool is a built-in utility that can help remove temporary files and system clutter, indirectly helping clean up some registry associations linked to uninstalled programs.
How to use Disk Cleanup:
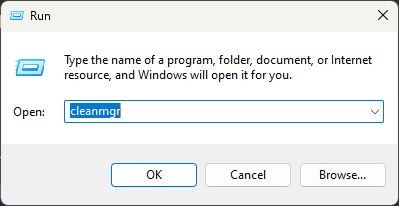
- Press Win + R, type cleanmgr, and press Enter.

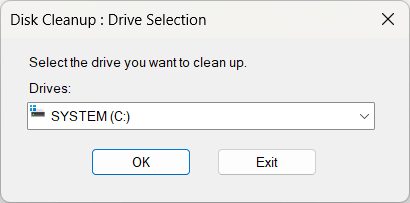
- Select the C: drive and click OK

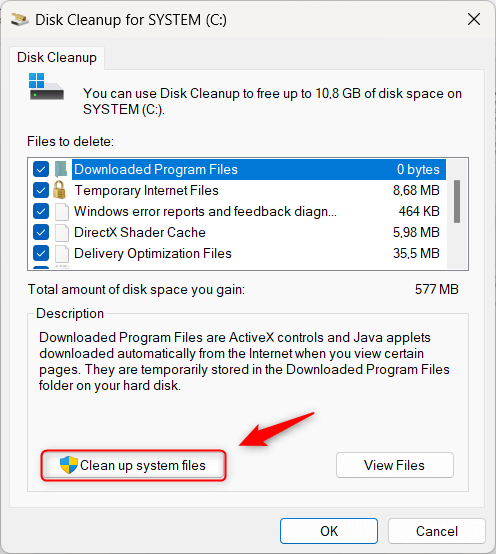
- Click on Clean up system files for a more thorough scan.

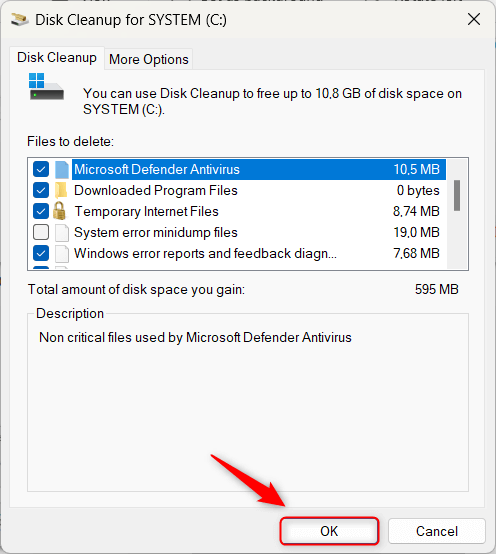
- After the scan, check the boxes for the items you wish to delete and click OK.
- Confirm the action by clicking Delete Files.

2. Using Third-Party Registry Cleaners
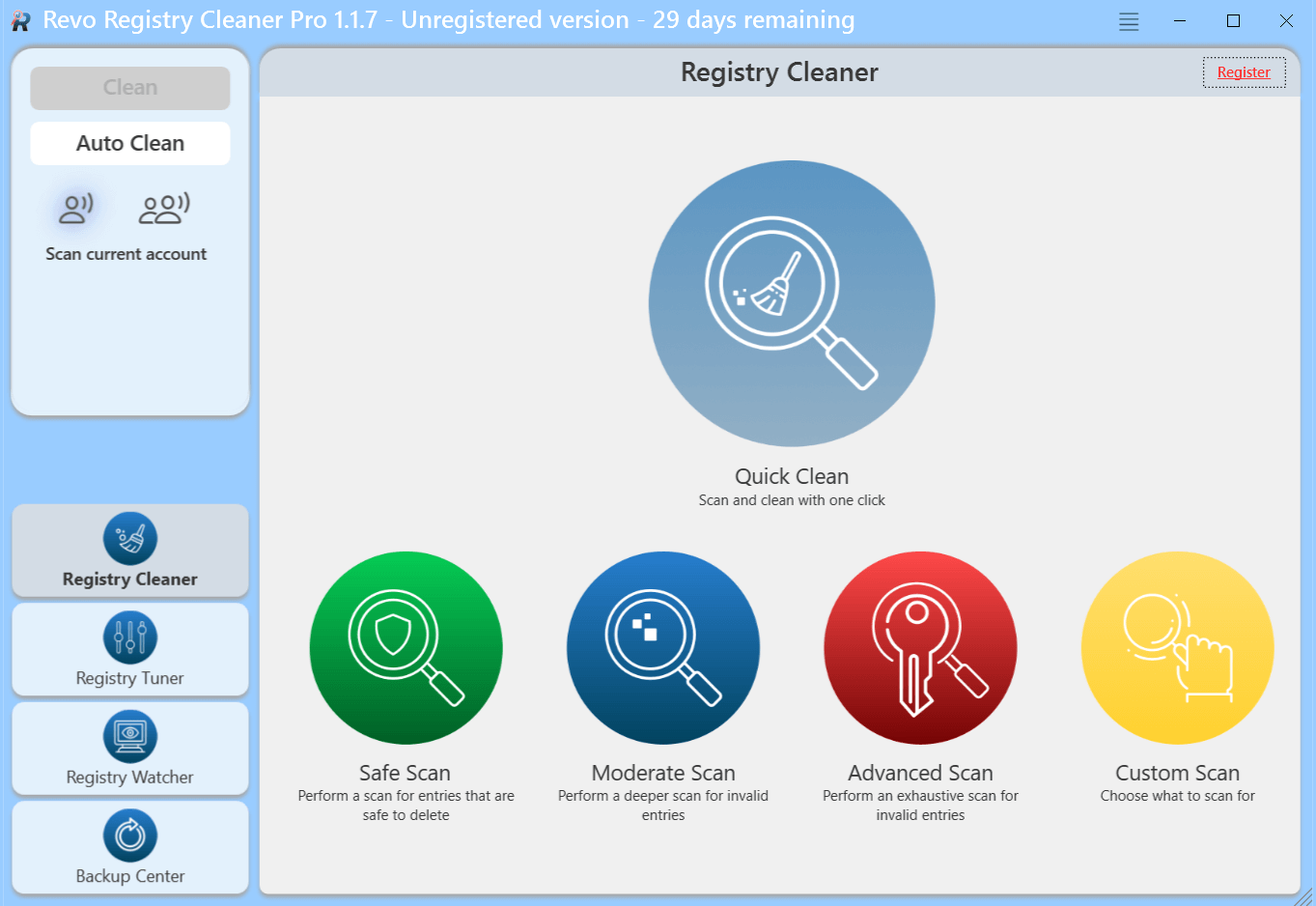
Third-party registry cleaning utilities are software tools designed to scan the Windows Registry for invalid or obsolete entries and remove them automatically. Popular option is Revo Registry Cleaner.
How to use third-party registry cleaners:
- Download and install Revo Registry Cleaner
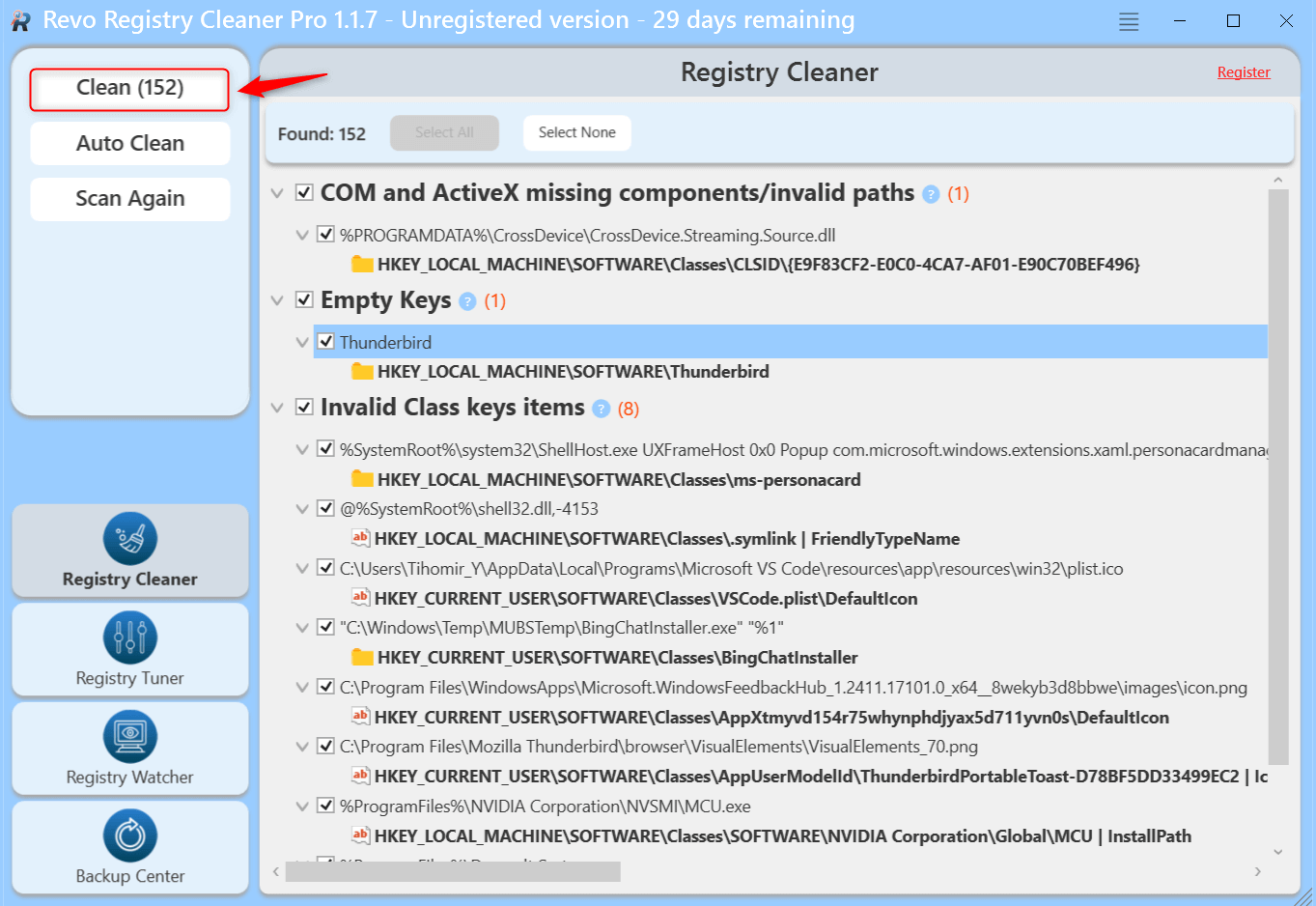
- Run a Safe Scan or any other of the scan modules for more in depth cleaning.

- Review the list of detected issues, and choose which entries to clean or remove.

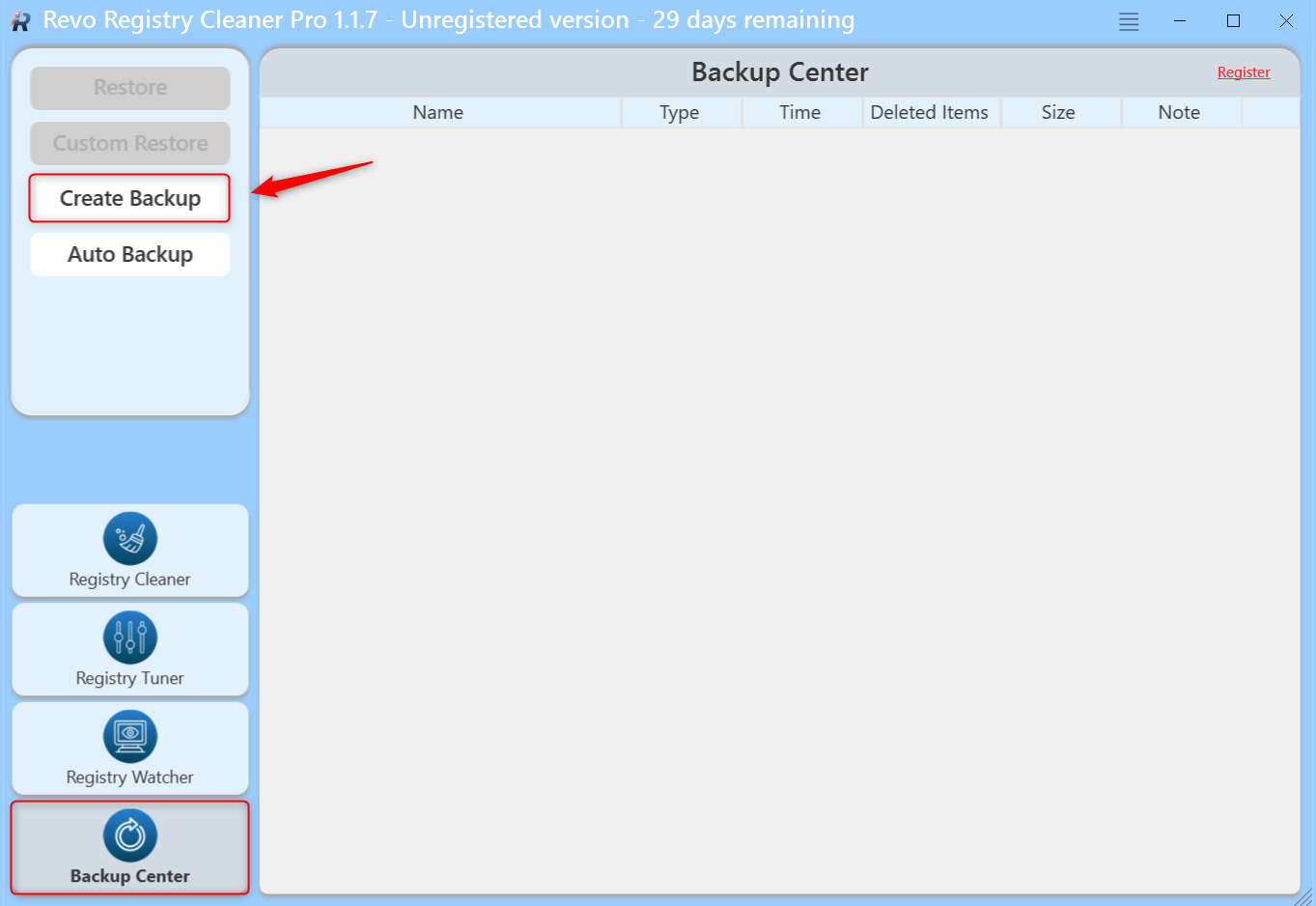
- Make sure to create a full Registry Backup by going to the Backup Center before making any changes, which is highly recommended.

While the majority of these Registry cleaning tools can be overly aggressive Revo Registry Cleaner excels at protecting your registry files ensuring that you can safely view, delete and modify your Registry entries.
3. Manually Clean the Registry Using Registry Editor
If you’re comfortable with advanced system maintenance, you can manually delete obsolete entries in the Registry.
Steps for manual cleaning:
- Open Registry Editor as described earlier.
- Use the Find function (Ctrl + F) to search for remnants of uninstalled programs.
- Carefully review the search results and delete unnecessary keys or values related to software you no longer use.
Note: Deleting the wrong entries can cause system instability. Only remove keys you are confident are no longer needed.
4. System Restore
If cleaning the Registry manually or with a third-party tool causes unexpected problems, you can use System Restore to roll back your system to a previous state, including the Registry.
How to perform a system restore:
- Type Create a restore point in the Windows search bar and open the System Properties window.
- Click on System Restore, and follow the prompts to revert your system to a previous restore point.
System Restore will undo any changes made to the Registry since the restore point was created, offering a safety net if things go wrong.
Conclusion
Cleaning the Windows Registry can help improve system performance and resolve certain errors, but it should be done with caution. Always back up the Registry before making any changes and consider using built-in tools like Disk Cleanup or third-party registry cleaners for safe and effective cleanup. For advanced users, manual registry editing offers more control but comes with the risk of system instability if handled improperly. With proper care, you can maintain a clean and efficient Windows Registry, ensuring your system runs smoothly.

No Comments